Intestinal Biotic Bio-Regulator Complex Eukaryotes extracted from roots - Lapis Pro
Written by Fulmina Institut
This narrative was written by “Fulmina Institut.” Some of the explanations for the scientific and medical terms are excerpts of the Wikipedia Foundation to whom we wish to give credit.
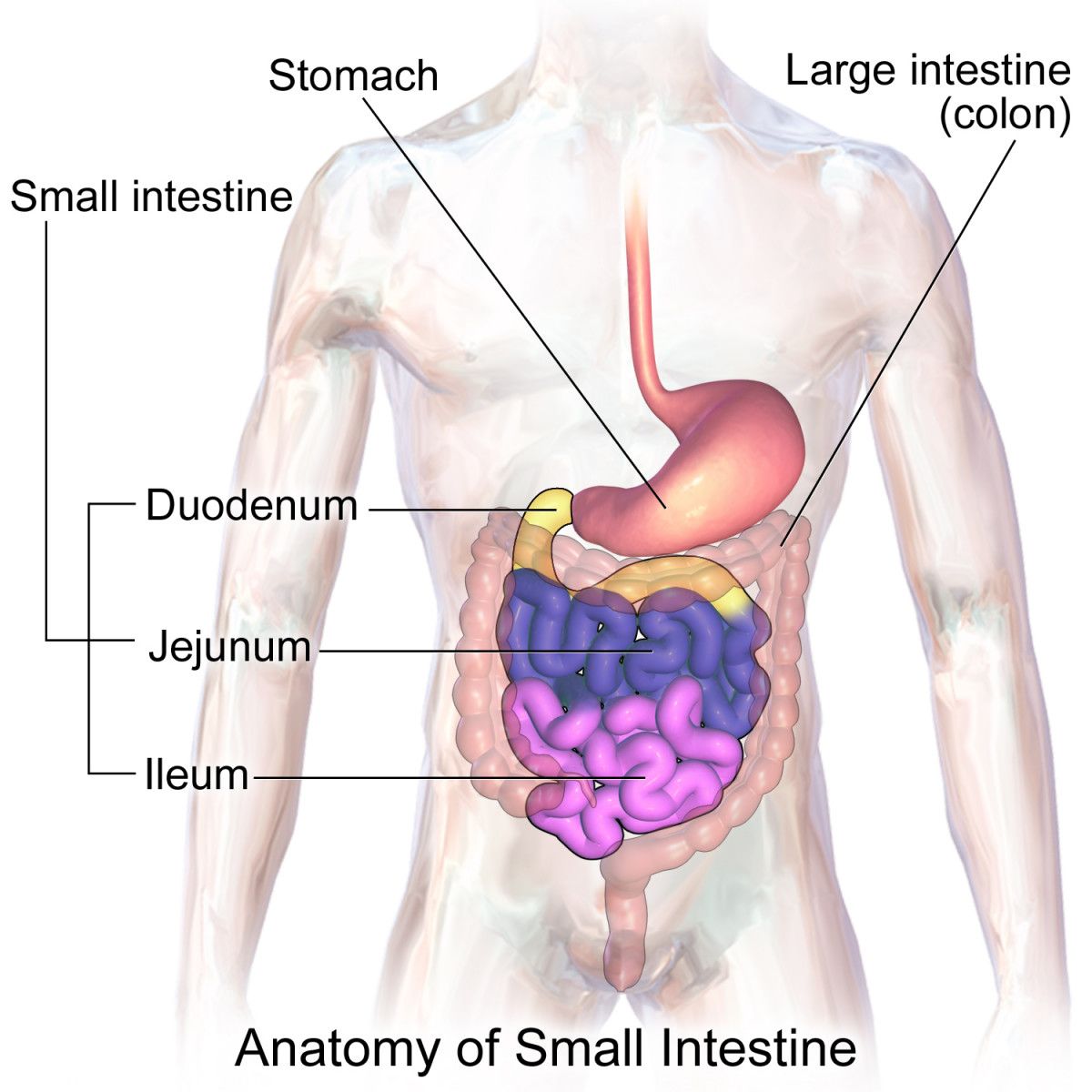
Our intestine has an extraordinary and incredible set of functions. It contains almost one hundred billion micro-organisms : ten times more than the number of cells of our organism !
The length of the intestine measures from 7 to 8 meters. The surface of the intestinal mucosa is approximately 300 to 400 square meters and it represents the largest absorption and exchange surface of the human body which is the basis of our immune defences and the energetic physical and cerebral potential.
The scientific world discovered since a few years that our intestine must be maintained in good health and that the intestinal flora is indispensable to the good functioning of our digestive system. The assimilation of the different nutrients that contain amino acids, vitamins, mineral salts, etc...are all necessary for the maintenance of our cellular and organic survival. With aging, our intestine accumulates toxins, heavy metals, and grows adhesions and polyps, and the mucosa walls become thinner. They become more sensitive to the different toxic particles and their capacity to assimilate is diminishing. The PH balance is unstable and the enzymatic exchanges diminish. The intestinal biotic bio-regulators extracted from different roots, will regulate these deficiencies.
Caused by the advances in metagenomics, we have discovered the role of multiple organisms prokaryotes, bacteria, viruses and eukaryotes that are at the origin of the evolutive chain of our life and that we find today in our intestines. The later need to be respected, nourished and regenerated since it is the source of a good metabolism, a good health, a good immunity, a good nervous system, therefore by the effects of stress regulation, of a good digestion of fats, sugars, etc... Its bad functioning is provoking allergies (skin illnesses), inflammatory illnesses, all kinds of disequilibrium, organic and cellular degeneration.
These complex of intestinal biotic bio-regulators from vegetal origin that are constituted of eukaryotes, are issued from new fundamental applied research in meta genomic. These biotic bio-regulators permit a natural relaunch our immune system without the addition of prebiotics nor probiotics.
Recall :
Biotics (from Latin bioticus) 1- Is said for any factor that is related with the development of life. Whatever is biotic, will develop in an environment where life can develop. The biotic is an electrodynamic field linked to the bio-membranes of the prokaryotes cells and the bio-membranes of mitochondria as well as to the cells of the eukaryotes. The field of electro-dynamic action is provoked by the effects of the fluctuations (perturbations) of the electromagnetic field on the photons, the electrons, the protons and the ions via the specialized molecules of the intestinal functions, among others.
The prebiotics are generally oligosaccharides or short chained polysaccharides constituted approximately from two (2) to twenty (20) units of sugar. They escape digestion in the small intestine and are potential substrates for the hydrolysis and the fermentation by the intestinal bacteria. Pre-biotics must act as selective substrates of one or a restricted number of beneficial bacterial strains residing in the colon and stimulate their growth. The bifidobacterium and the lactobacilli are the micro-organisms of the intestinal microbiota (intestinal flora) most frequently targeted.
The probiotics are acting by a set of different mechanisms. They modulate the activity of the intestinal immune system, by reinforcing the immunity when it is weak, for example in children or in old age person. By opposition, they can diminish the over activation of the immune system, in case of allergies or inflammatory diseases of the intestine. The barrier function of the intestinal mucosa (wall) is in fact improved, by the augmentation of the production of mucus or antibodies of type IgA3. They have direct anti-pathogenic effects by preventing the adhesion of pathogenic agents to the mucosa wall of the intestine.
These bacteria or yeasts help digestion and stimulate the immune and regenerative system of the organism.
In order for the probiotics to have a beneficial effect on health, many conditions must be reunited :
They must be alive, natural and of good quality ;
The good strains must be selected to produce the desired effect: there exists thousands of strains and each of them has a specific effect ;
That each selected strain has shown its capability to resist to bile and gastric acid.
In fact, “to be efficient on the intestinal flora” these biotic bio-regulators active principles must gene-rate or favour the development of life and become active in the colon and “in sufficient quantities”. They should not be degraded following their passage into the stomach, and “must be capable of resisting gastric acidity and pancreatic sugars”.
Explanation of the action of an intestinal biotic bio-regulator :
Life sciences and understanding of biophysical functions : biophysics is a discipline at the interface of physics and biology where the observation tools of physical phenomena are applied to molecules of biological origin. Several areas of biology in its broadest sense have benefited from advances in biophysics : medicine, cellular biology or molecular biology are but a few examples of the application of the understanding of biophysics.
Understanding the cellular functions of our body contributes greatly to the development of natural health products against aging and the apoptosis of our cells.
Apoptosis (or programmed cell death) is the process by which cells trigger their self-destruction in response to a signal. This is one possible way of cell death, which is physiological, genetically programmed, and necessary for the survival of multicellular organisms. It is in constant balance with cell proliferation.
The answer to questions relative to the functions of biological physical life must be sought in the origin of the organization of our cell functions and of the energy that drive them (light).
The human body is a valuable natural treasure and its potential is phenomenal. It is the temple of Man and of our consciousness, therefore only a golden key can unlock its mysteries :
Aging is a biological phenomenon.
Cells constantly reproduce, grow old and die (apoptosis).
We all gradually grow to adulthood and then to old age.
We are generally in good health up to our fifties; the cells that form our bodies are still very active. With increasing age their energy potential weaken and our cells begin to lose their vitality. Toxins (a toxin is a toxic substance affecting one or more living organisms), and free radicals (chemical species having one or more electrons whose chemical bond may be broken. When broken by heterolytic, it produces ions rather than radicals) accumulating in cell functions and in the bloodstream, cause a decrease in the immune recognition systems in terms of both qualitative and quantitative reactions.
This aging process negatively affects the general functions of assimilation and distribution of cellular energy, decreasing the speed and the quality of cellular reproduction of our body functions. The energy needed for biological binding and for the transmissions functions of internal membranes weakens.
The quality of the exchanges of energy within the cells to ensure their replication, and the correct information of the DNA and mitochondrial DNA to RNA / mRNA toward the various proteins in support of the synthesis of amino acid becomes underperforming (the human body is composed of 20% protein. Proteins belong to the family of protids, and play a key role in virtually all biological processes. Proteins are tiny molecules consisting of amino acids).
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins which then become less efficient. Different decisive qualitative and quantitative factors determine information, rate and the extent of the overall aging of the body.
The cleaning mechanism of cell toxins as well as the level of energy for good mitochondrial function leading to a good reproduction of the cellular chain for our different organs diminishes.
Mitochondria are organelles present in the vast majority of cells (eukaryotes). They are derived from the endosymbiosis of alpha-proteobacteria thought to have occurred about two billion years ago (endosymbiotic theory). During the evolution, mitochondria have retained their own genome, which although very small compared to that of a bacterium, is essential to the proper functioning of these organelles. Confined within mitochondria, organelles producing cellular energy, the mitochondrial genome (mtDNA) is distinct from the DNA contained in the nucleus.
It is therefore necessary to prevent telomere shortening since they contribute to the stability of the structure of the DNA and, if impaired, will cause aging. Its protective role must be maintained so that the cell does not interpret the information as a corruption of the DNA, and does not cause senescence or termination of the growth that is in close relation with the duration the life of the cell.
A telomere is a highly repetitive region, so an a priori non-coding DNA at the end of a chromosome. Whenever a chromosome stick is duplicated, during the replication process, which precedes the mitosis (cell division), the enzyme complex of the DNA polymerase is unable to copy the last nucleotides : the lack of a good operation of telomeres would mean the rapid loss of genetic information necessary for the cellular function. Telomeres shorten with age, inflammation and stress.
Studies have shown that short telomeres are associated with a higher risk of age-related diseases.
All these biological phenomena are manifestations that appear during the renewal process and the gradual aging of cells: modification of information of DNA, bonds of molecules, protein oxidation, glycosylation, which is of great importance in signaling and for good recognition of cellular immune functions information.
Glycosylation is an enzymatic reaction which consists in covalently linking a carbohydrate to a peptide chain, a protein, a lipid or to other molecule. Glycosylation essentially relates to membrane proteins as well as secreted proteins.
Research by Russian and American scientists such as Aleksei Glomikov, the foremost pioneer in this field, Prof. Vladimir Khavinson, Elizabeth Blackburn, Carol Greider and Jack Szostak who elucidated the physical mechanisms of cellular aging (2009 Nobel Prize) indicates that this process can be likened to a disease.
Our body suffers from the disease of premature aging which causes organic, neuroendocrine, immune metabolic disorders, etc.
Biological fluids exchanges slow down resulting in wrinkles, age spots characterized by the accumulation of lipofuscin, a pigment resulting from the degradation of cellular organelles. Nutritional exchanges weaken and lead to metabolic disorders and decreased energy and vitality
These problems are the result of multiple energy deficiencies: physical, emotional and mental disorders in humans. The premature physical aging finds its origin in the deficiency of a quantitative and qualitative supply of energy at the level of the mitochondrial cell and that of its mitochondrial DNA.
Energy : its role is paramount physiologically ; it is in the mitochondria that (organic) energy molecules will be recovered.
Mitochondria are responsible for producing the energy needed for vital functions. They perform a very important biochemical and bio-electro-chemical conversion process and provide the metabolic function channels for cellular respiration. It is at this level that energy is released. Mitochondria are dubbed “the nuclear power plants of the cells” and ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the cell energy reserves.
The primary role of adenosine triphosphate is to provide the energy needed for chemical reactions of cells. It is a nucleotide that is used to store and transport energy.
Mitochondria contribute to the transmission of intercellular (mitochondrial DNA) information by playing a role in cell differentiation. They are able to regulate cycles and cell growth. The amount of mitochondrial cells in the cell depends on its metabolism; the more rigorous and important the activity, the higher the number of cells and of mitochondrial organelles. These strengthen the body’s vital organs and their functions.
Mitochondria convert oxygen to release the energy necessary for the body. During these transformation and normal cell “tonic” operation processes, there appears oxidative stress that produces free radicals. Free radicals concentrate their attack on the fatty acids of cell membranes and on DNA. This can cause irreversible damage to the membrane of mitochondrial DNA.
It is noteworthy that vitamins A, C and E do neutralize free radicals (if they are natural and of a very good quality) by providing the necessary electrons.
When the concentration of these free radicals is not too high, our antioxidant system has the complex ability to fully drain these superoxides. To respond to aggression (oxidative stress) our body produces certain proteins, “heat shock proteins” that protect the mitochondria of aggression stress [heat shock proteins or HSP (for heat shock proteins) are a class of chaperone proteins originally discovered because of their accumulation and their inducibility by heat effect. Their role consists in protecting, maintaining and regulating the protein function of the cells with which they are associated...] .
Normally, antioxidants protect the cells but they can also suffer various injuries, and based on age, they may not completely assume the protection of mitochondrial functions.
Antioxidants do not penetrate mitochondrial membranes, and when fragments are missing, the direct energy function of ATP ASE diminishes causing a decrease of the functions of the overall biochemical metabolism.
This understanding of the processes involved with physical and biochemical molecules, cells and organs has made possible a natural regeneration therapy : an intestinal biotic bio- regulator complex.
When scientists carried out the gene transfer process, they revealed a biologically active substance called ions. These are highly energetic particles. An ion is an electrically charged chemical species - an atom or a groups of atoms - which has won (or lost) one or more electrons. Thus an ion cannot be electrically neutral. The value of the electric charge is indicated as a superscript at the end of the chemical formula of the ion, in a multiple of the elementary electrical charge
The intestinal biotic complex highly energetic : a natural organism extract with high longevity whose biological and cellular ionic structure is linear, and features an ionic energy charge capable of absorbing and releasing high energy levels.
It is the most powerful catalyst support and carrier / transformer of biological energy in today’s world but its origin and its empirical use dates back to antiquity.
These bio-physical particles are highly energetics, it has an inherent function of transformation and liberation of bio-electric charges and of acceleration of the photons [this is the quantum of energy associated with electromagnetic waves (from radio to gamma rays passing through the visible light), which exhibits some characteristics of elementary particles. In quantum field theory, the photon is the media-tor particle of electromagnetic interactions. In other words, when two electrically charged particles interact, the interaction results in a quantum point of view as an exchange of photons]. Thus result of such reaction is called : an ion article.
This substance being activated through the principle of transformation mechanisms enabled by the provides ongoing energy to mitochondrial and general biogenic functions of organs in a succession of steps.
When the active ingredients of a biotic bio-regulator complex cross the cell membrane through natural attraction, the bio-electric energy principles are stimulated by this load This provides a high intrinsic energy of 60 microvolts (1 microvolt = 1 millionth of a volt) which will reach, after melting and absorption through the liposome, an energy charge of 180 microvolts. This charge is immediately transferred into the mitochondria.
[The name liposome is derived from two Greek words: ‘Lipos’ meaning fat and ‘Soma’ meaning body. Liposomes were described in 1961 by British biophysicist and hematologist Dr. Alec Bangham Felow Douglas of the Royal Society at the Babraham Institute in Cambridge (published 1964). A liposome can be formed at a variety of sizes as uni-lamellar or multi-lamellar construction, and its name relates to its structural building blocks, phospholipids, and not to its size. In contrast, the term Nanosome does relate to size and was coined in the early 1990s to denote special liposomes in the low nanometer range; liposome and Nanosome are not synonyms. A liposome does not necessarily have lipophobic contents, such as water, although it usually does. This characteristic allows liposomes to be used as vectors or carriers in pharmacology (vectorization of active ingredients) and genetics (gene transfer)]
This release produces a 180 mv energy conversion. The mitochondrial functions hence benefit from a sufficient charge to allow them to extend their lifespan, and to durably maintain cellular and organic functions. They will eventually return to a load of 60 mv, ion particles having a recurring function. Within the cell, these particles maintain an energy capability over a period of about 10 days ; they are then eliminated through the lymphatic system. This phenomenon shows no alteration, change or any negative effect on the cell membrane.
The lymphatic system functions in such a way that the whole body, with the exception of the central nervous system, the muscles, the cartilage and the bone marrow, possesses an array of lymphatic vessels operating in parallel to the veins and following the network of arteries.
The lymph, an interstitial fluid circulating in the lymph vessels, will load up a portion of the waste produced by cellular activity via the intercellular tissue. The lymph is purified by passing through the [lymph] nodes. It then travels toward the bloodstream which will be reached by the thoracic duct at the level of the subclavian veins.
The lymphatic system is responsible for transporting most of the fat (lipids) ingested into the bloodstream, hence allowing it to bypass the liver.
The direct action of an intestinal biotic bio-begulator complex allows the lymph to actually absorb this source of supply very rapidly, hence obtaining a faster, more sustainable regeneration process, and all of it without any negative ramification.
The active ingredients of the complex may be used for the absorption of precipitation of calcium phosphate particles in the cell membrane.
The active ingredients can enter the mitochondrial cell membrane as they have the necessary intrinsic bioelectric load of 180 mv. instead of a load of 60 mv.
When penetrating the cell membrane, the ion particle can use the difference in the bio-electrical potential of the cell membrane ; in other words it can use particles of calcium, and even more so of gold due to its vibratory qualities.
It can also use other metals, mainly lead, tin, copper, iron, silver, antimony and mercury : these particles found in micro quantities act as vibration receivers capturing the information conveyed by the chelating carriers which spontaneously absorb the informative energy produced for the DNA / DNA messenger and mitochondrial DNA in order to generate this major transmuting energy potential deployed for regeneration by the initial information, and then reprogram the general organic activation .
Re-call : chelation is a physico-chemical process which involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand*, known as a chelating agent and a metallic cation (or central atom) that has become complexed and said to be chelated. It is noteworthy that chelating metals are found in trace quantities.They do, however play an important role as vibration keys in reading the registry of the various DNA chapters; They react by opening or closing based on frequency pulses received in picoseconds from 8x8 up to 64x8 picosecond indicating a level modification inducing a geometrical modification of the directional vector inducing a geometrical modification of the direction vector in space.
*In biology, a ligand (from the Latin, binder) is a molecule which binds in a reversible manner onto a target macromolecule, a protein or a nucleic acid, usually play a functional role: structural stabilization, catalysis, modulation of enzymatic activity, and signal transmission.
The intestinal biotic bio-begulator complex can transform a cell and bring our intestines from a weak state to an optimal state of energy.
Its action is physical, and as a consequence it impacts positively both emotion and mind.
It allows the body to go from a state of aging and disease to a state of vibrant health and vitality.
Regeneration of the skin and organs; positive action on the side effects linked to various diseases, and therapeutic action on various pathologies.
Improves immune and hormonal functions; regeneration of the brain, improved sleep, muscle restructuring, etc.
Copyright Fulmina Foundation
Powered by Froala Editor
